[Algorithm/Java] 백준 1713번 - 후보 추천하기
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1713
🔍 문제 풀이
Flowchart
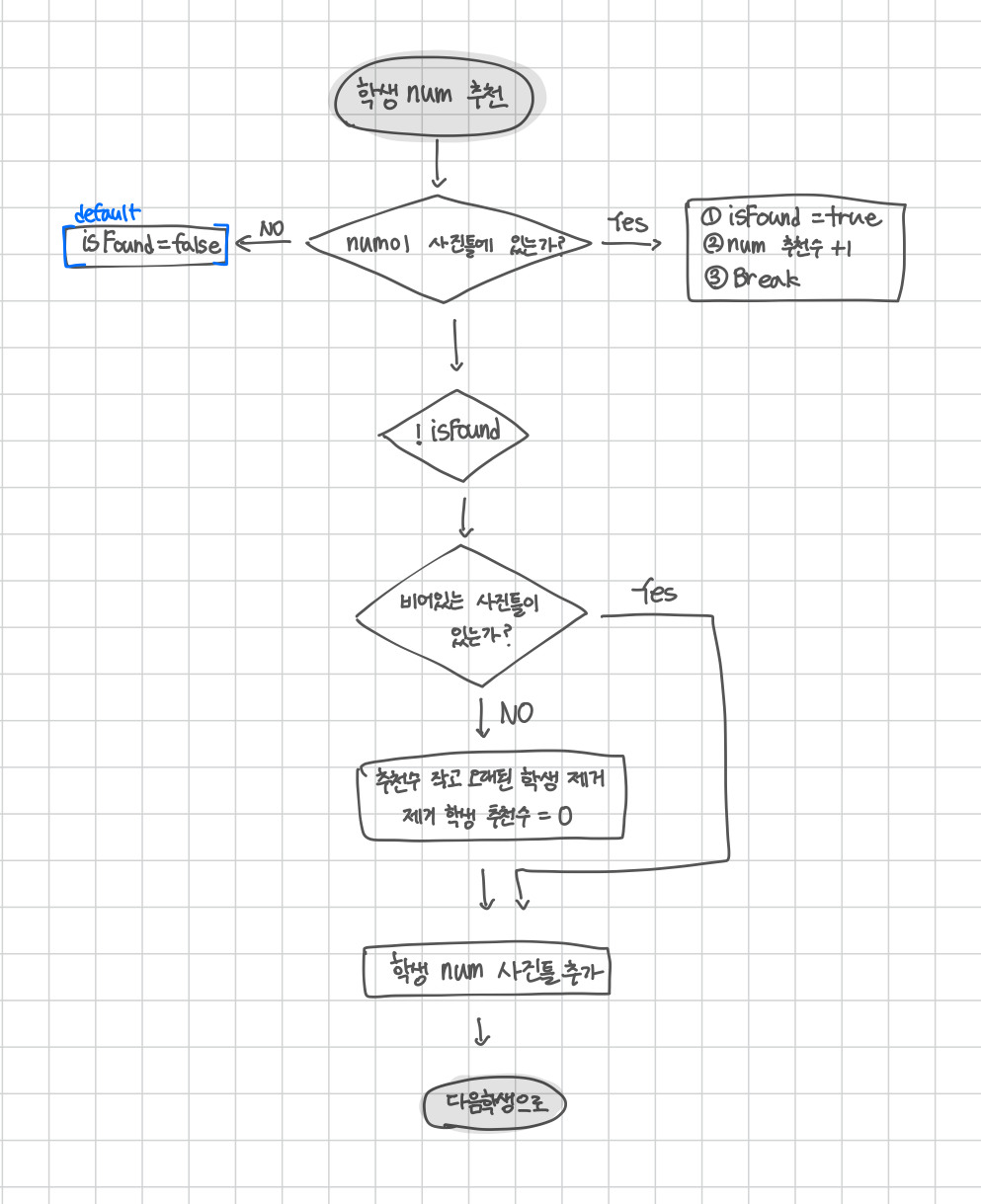
배운 점
class를 만들어야 하는 조건
- 정보가 2개 이상 묶여 움직일 때
- 배열/Map은 각각 따로 관리해야 하지만, 클래스는 한 덩어리로 관리 가능
- 정렬 기준이 여러 개일 때
- 클래스를 써야 sort()에서 Comparator로 정렬이 쉬움
- 찾기, 수정, 삭제가 자주 필요할 때
- 클래스를 써야 객체 단위로 비교/수정/삭제가 쉬움
- e.g., 같은 학생을 찾아서 추천 수 증가, 리스트에서 조건에 맞는 항목만 제거
❓ 클래스를 꼭 처음부터 만들어야 하나?
일단 간단하게 구현해 보고, 복잡해질 때 클래스 도입하자
예시를 들어보겠다.
- 처음엔
List<Integer>혹은Map<Integer, Integer>로 시작 - 그런데 추천 수도 저장해야 함
Map<Integer, Integer> recommendMap
- 시간도 저장해야 함
Map<Integer, Integer> timeMap
- 근데 이걸 기준으로 정렬까지 해야 함 -> 🌀 복잡해진다…
💡 이럴 거면 그냥 Student 클래스 하나 만들자!
class 사용의 필요성
처음에는 복잡해 보였지만, 클래스를 쓰니 오히려 더 깔끔하고 이해하기 쉬운 코드를 만들 수 있었다.
이 문제에서는 학생마다 다음과 같은 정보를 관리해야 한다.
- 번호 (num)
- 추천 횟수 (recommend)
- 게시된 시간 (time)
이 세 가지 정보를 동시에 다뤄야 하기 때문에, 하나의 객체로 묶어 관리하는 것이 효율적이다.
따라서 Student 클래스로 구조화하는 것이 적절하다.
배열이나 Map만으로는 이걸 한꺼번에 다루기가 어렵다.
만약 클래스를 쓰지 않고 코딩하면, 이런 식으로 3개의 배열을 따로 둬야 한다.
int[] nums = new int[N]; // 번호
int[] recommends = new int[N]; // 추천수
int[] times = new int[N]; // 시간
이렇게 여러 배열을 각각 관리하면
추천 수가 가장 적고, 오래된 학생을 찾기 위해 세 배열을 동기화해서 탐색해야 하기 때문에, 리스트 정렬도 어렵고 비효율적이다.
클래스를 사용하면?
class Student {
int num; // 학생 번호
int recommend; // 추천 수
int time; // 게시된 시간
Student(int num, int recommend, int time) {
this.num = num;
this.recommend = recommend;
this.time = time;
}
}
이렇게 만들면 List<Student>로 관리하면서 sort()도 편하게 쓸 수 있고, 특정 학생을 찾거나 수정하기도 쉬워진다.
정렬도 매우 간단하다.
frame.sort((a, b) -> {
if (a.recommend == b.recommend) return a.time - b.time;
return a.recommend - b.recommend;
});
List 구조
List<Student>란, Student 객체를 담는 리스트를 의미한다.
리스트에는 Student 객체들이 들어 있다. 예를 들어, 아래와 같은 코드가 있다고 가정하면,
List<Student> frame = new ArrayList<>();
frame.add(new Student(2, 1, 0));
frame.add(new Student(5, 3, 1));
위 상태에서 frame은 이렇게 생긴 구조이다.
frame = [
Student(num=2, recommend=1, time=0),
Student(num=5, recommend=3, time=1)
]
즉, frame 리스트의 각 요소는 Student라는 객체이고,
그 객체는 내부에 다음과 같은 변수(필드) 들을 가지고 있다.
| 필드명 | 값 (예시) |
|---|---|
num |
2 |
recommend |
1 |
time |
0 |
그래서
s.num,s.recommend이런 식으로 접근이 가능한 것이다.
for (Student s : frame) {
System.out.println(s.num); // 학생 번호 출력
System.out.println(s.recommend); // 추천 수 출력
System.out.println(s.time); // 게시된 시간 출력
}
💻 전체 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Student {
int num; // 학생 번호
int recommend; // 추천 수
int time; // 게시 시간
public Student(int num, int recommend, int time){
this.num = num;
this.recommend = recommend;
this.time = time;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); // 사진틀 개수
int total = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); // 총 추천 횟수
int time = 0;
List<Student> frame = new ArrayList<>();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<total; i++) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
boolean isFound = false;
// 1. 학생 num이 사진 틀에 있는가?
for (Student s : frame) {
// yes -> 추천수 증가
if (num == s.num) {
isFound = true;
s.recommend++;
break;
}
}
// no -> 추가 로직 실행
if(!isFound){
// 2. 사진들이 꽉 찼는가?
if (frame.size() >= n) {
// yes -> 추천 수 오름차순, 같으면 시간 오름차순 정렬
frame.sort((a, b) -> {
if (a.recommend == b.recommend) return a.time - b.time;
else return a.recommend - b.recommend;
});
frame.remove(0);
}
// 삭제 여부와 관계없이 새 학생은 추가
frame.add(new Student(num, 1, time++));
}
}
// 최종 학생 번호 정렬 후 출력
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Student s : frame) {
result.add(s.num);
}
Collections.sort(result);
for (int val : result) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
}
}

댓글남기기