[Algorithm/Java] 백준 2178번 - 미로 탐색
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2178
🔍 문제 풀이
문제 도식화
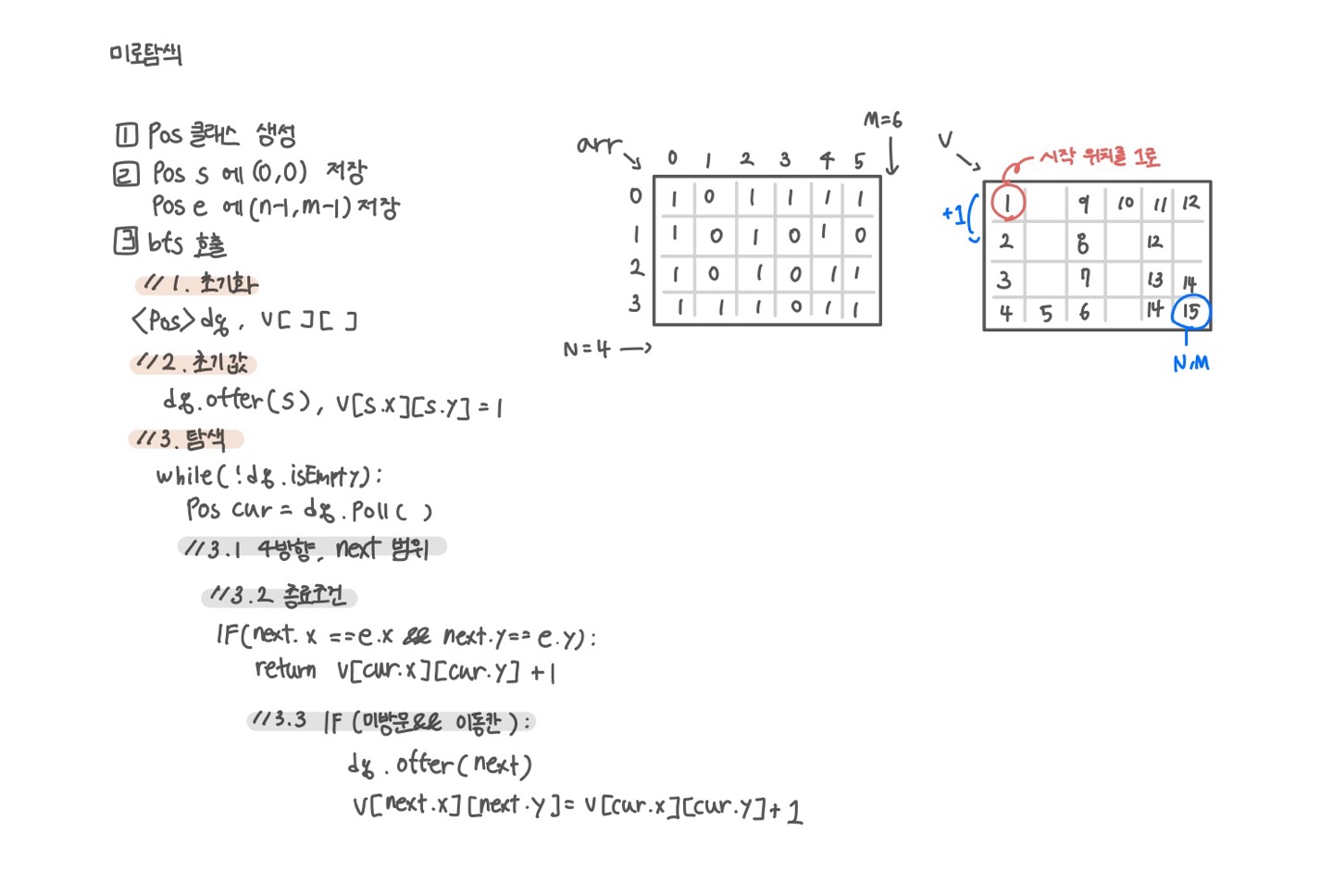
💻 코드
전체 코드
클래스 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int n, m;
static int[][] arr;
static int[][] v;
static Pos s, e;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = line.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
s = new Pos(0, 0);
e = new Pos(n-1, m-1);
int ans = bfs();
System.out.println(ans);
}
static int bfs() {
// 1. 초기화
Deque<Pos> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
v = new int[n][m];
// 2. 초기값
dq.offer(s);
v[s.x][s.y] = 1;
// 3. 탐색
while(!dq.isEmpty()){
Pos cur = dq.poll();
// 3.1 4방향, next 범위
for(int d=0; d<4; d++){
Pos next = new Pos(cur.x + dx[d], cur.y + dy[d]);
if(next.x < 0 || next.x >= n || next.y < 0 || next.y >= m) continue;
// 3.2 종료 조건
if(next.x == e.x && next.y == e.y) {
return v[cur.x][cur.y] + 1; // 도착 칸 포함
}
// 3.3 미방문 && 이동칸
if(arr[next.x][next.y] == 1 && v[next.x][next.y] == 0){
dq.offer(next);
v[next.x][next.y] = v[cur.x][cur.y] + 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
static class Pos {
int x, y;
Pos(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}
클래스 미사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[][] arr;
static int[][] v;
static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = line.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
int ans = bfs();
System.out.println(ans);
}
static int bfs(){
// 1. 초기화
Deque<int[]> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
v = new int[n][m];
// 2. 초기값
dq.offer(new int[]{0, 0});
v[0][0] = 1;
// 3. 탐색
while(!dq.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = dq.poll();
int cx = cur[0];
int cy = cur[1];
// 3.1 4방향, nx와 ny 범위
for(int d=0; d<4; d++){
int nx = cx + dx[d];
int ny = cy + dy[d];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
// 3.2 종료 조건
if(nx == n-1 && ny == m-1){
return v[cx][cy] + 1;
}
// 3.3 미방문 && 이동칸
if(arr[nx][ny] == 1 && v[nx][ny] == 0){
dq.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
v[nx][ny] = v[cx][cy] + 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
스켈레톤 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[][] arr;
static int[][] v;
static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = line.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
int ans = bfs();
System.out.println(ans);
}
static int bfs(){
return 0;
}
}

댓글남기기