[JS] 배열과 메서드
1. 배열 개요
1.1 배열의 개념
배열은 여러 값을 하나의 변수에 저장할 수 있는 자료 구조이다.
연관된 데이터를 정리정돈해서 단순화시키기 위해 배열을 사용한다.
1.2 배열의 특징
- 순서가 있다.
- 배열에 저장된 각 항목은 특정 순서를 가지며, 이 순서는 0부터 시작하는 인덱스로 표현된다.
- 배열에 저장된 각 항목은 특정 순서를 가지며, 이 순서는 0부터 시작하는 인덱스로 표현된다.
- 다양한 데이터 타입을 저장할 수 있다.
- 숫자, 문자열, 객체, 심지어 다른 배열까지도 배열에 저장할 수 있다.
- 숫자, 문자열, 객체, 심지어 다른 배열까지도 배열에 저장할 수 있다.
- 동적 크기
- 자바스크립트의 배열은 크기가 고정되어 있지 않는다. 필요에 따라 자동으로 확장되거나 축소된다.
1.3 인덱스와 요소
- 프로그래밍에선 자릿수를 인덱스라고 한다. (첫 번째 index는 0부터 시작)
- 배열 내부에 든 값을 요소라고 한다.
- 아래 코드 배열 value에서
smile의 인덱스는 2이고, 배열의 요소의 개수는 4이다.
첫 번째 데이터인 sieun을 꺼내보자
const value = ["sieun", "Happy", "smile", "good"];
console.log(value[0]); // sieun출력
1.4 배열의 길이 구하기
배열은 배열의 길이(요소의 개수)를 나타내는
.length프로퍼티를 갖는다.
const value = ["sieun", "Happy", "smile", "good"];
console.log(value.length); // 4출력
2. 배열의 생성
new Array()와 Array.of()는 주로 새로운 배열을 생성할 때 사용되고, Array.from()은 기존 객체를 배열로 변환할 때 주로 사용된다.
2.1 배열 리터럴 대괄호([ ])를 사용
빈 배열 생성
const arr = [];
arr[0] = "sieun";
arr[1] = "happy";
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i]); // sieun, happy 출력
}
초기 값할당하여 배열 생성
const arr = ["sieun", "happy"];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i]); // sieun, happy 출력
}
2.2 new array()
new Array() 함수를 사용하여 빈 배열이나 지정한 길이의 배열을 생성할 수 있다.
빈 배열 생성
const arr = new Array("sieun", "happy");
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i]); // sieun, happy 출력
}
지정한 길이의 배열 생성
const arr = new Array(3);
2.3 array.of()
전달한 인자들(파라미터들)을 사용하여 새로운 배열을 생성하는 메서드이다. 즉, 이 메서드는 인자 값을 배열의 요소로 만든다.
const arr = Array.of("sieun", "happy");
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i]); // sieun, happy 출력
}
2.4 array.from()
3. 배열 메서드
3.1 원본 배열을 수정하는 메서드
| 원본 배열을 수정하는 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
push() |
배열의 끝에 하나 이상의 요소 추가 및 길이 반환 |
pop() |
배열의 마지막 요소 제거 및 반환 |
shift() |
배열의 첫 번째 요소 제거 및 반환 |
unshift() |
배열의 시작 부분에 요소 추가 및 길이 반환 |
splice() |
배열의 요소 삭제 또는 추가하여 내용 변경 |
// 배열의 끝에 'orange' 추가하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
fruits.push("orange");
console.log(fruits); // [ 'apple', 'banana', 'orange' ]
}
// 배열의 끝에 'orange' 제거하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
fruits.pop();
console.log(fruits); // [ 'apple', 'banana' ]
}
// 배열의 첫 번째 요소에 'apple' 추가하기
{
const fruits = ["banana", "orange"];
fruits.unshift("apple");
console.log(fruits); // [ 'apple', 'banana', 'orange' ]
}
// 배열의 첫 번째 요소인 'apple' 제거하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
fruits.shift();
console.log(fruits); // [ 'banana', 'orange' ]
}
// 배열의 'banana' 요소를 제거하고 'mange' 요소 추가하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
fruits.splice(1, 1, "mango");
console.log(fruits); // [ 'apple', 'mango', 'orange' ]
}
spile() 자세히 알아보기
① 배열의 요소 삭제 또는 추가하여 내용을 변경하는 메서드이다.
const arr = ["시", "은", "바", "보", "입", "니", "다"];
arr.splice(2, 2, "천", "사");
console.log(arr);

② 값을 삭제하지 않고 중간에 값을 추가할 수 있다.
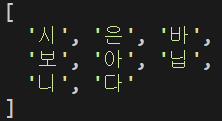
const arr = ["시", "은", "바", "보", "니", "다"];
arr.splice(4, 0, "아", "닙");
console.log(arr);
③ ⚠️단, 숫자 하나만 쓸 때는 뒤에 것을 다 지워버린다.
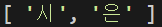
const arr = ["시", "은", "바", "보", "입", "니", "다"];
arr.splice(2);
console.log(arr);
3.2 새 배열을 반환하는 메서드
| 새 배열을 반환하는 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
map() ⭐ |
배열 내의 모든 요소에 대하여 주어진 함수를 호출한 결과를 모아 새 배열을 반환 각 요소는 새로운 요소로 매핑 항상 원본 배열의 길이만큼 반환, 반환값 없으면 undefined 출력 |
filter() ⭐ |
배열의 각 요소에 대해 콜백 함수를 실행하여 주어진 함수의 테스트를 통과하는 모든 요소로 이루어진 새 배열 반환 |
slice() |
배열의 일부를 얕은 복사하여 새 배열 객체로 반환 |
concat() |
기존 배열에 다른 배열 또는 값들을 합쳐서 새 배열 반환 |
// 배열의 각 요소에 2를 곱한 배열 만들기
{
const number = [1, 2, 3];
const doubled = number.map(function (num) {
return num * 2;
});
console.log(doubled); // [ 2, 4, 6 ]
}
// 짝수 요소들만 있는 배열 만들기
{
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const even = numbers.filter(function (num) {
return num % 2 === 0;
});
console.log(even); // [ 2, 4 ]
}
// 피자 조각 02, 03, 04만 잘라내어 배열 만들기
{
const pizza = ["🍕01", "🍕02", "🍕03", "🍕04", "🍕05", "🍕06"];
const sliced = pizza.slice(1, 3);
console.log(sliced); // [ '🍕02', '🍕03' ]
}
// 기존 배열에 'orange', 'mango'가 들어 있는 배열을 연결한 배열 만들기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
const moreFruites = fruits.concat(["orange,", "mango"]);
console.log(moreFruites); // [ 'apple', 'banana', 'orange,', 'mango' ]
}
3.3 결과값을 반환하는 메서드
| 결과값을 반환하는 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
reduce() |
배열의 각 요소에 대해 주어진 리듀서(reducer) 함수를 실행하고, 단일 결과값을 반환 리듀서(reducer)는 배열의 모든 요소를 하나의 값으로 축소하는 함수 |
find() |
배열의 각 요소에 대해 콜백 함수를 실행하여, 주어진 테스트 함수를 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 값을 반환 만족하는 요소가 없으면 undefined를 반환 |
some() |
배열의 어떤 요소라도 주어진 테스트 함수를 만족하면 true, 하나라도 만족하지 않으면 false 반환 |
every() |
모든 요소가 주어진 테스트 함수를 만족하면 true, 하나라도 만족하지 않으면 false 반환 |
includes() |
배열에서 특정 요소가 포함되어 있는지 여부를 true 또는 false로 반환 |
indexOf() |
배열에서 지정된 요소를 찾을 수 있는 첫 번째 인덱스 반환, 없으면 -1을 반환 |
lastIndexOf() |
indexOf()와 유사하지만 배열을 끝에서부터 검색 |
forEach() ⭐ |
배열의 각 요소에 대해 주어진 함수를 실행 배열을 순회하면서 각 요소에 대해 지정된 콜백 함수를 한 번씩 호출 map()과 달리 항상 undefined를 반환, retrun값 x |
// 배열의 요소를 모두 더한 값을 구하기
{
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const sum = numbers.reduce(function (acc, curr, idx) {
console.log(`acc: ${acc}, curr: ${curr}, idx: ${idx}`);
// acc: 0, curr: 1, idx: 0
// acc: 1, curr: 2, idx: 1
// acc: 3, curr: 3, idx: 2
// acc: 6, curr: 4, idx: 3
return acc + curr;
}, 0);
console.log(sum); // 10
}
// 배열에서 짝수 요소 구하기
{
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const fristEven = numbers.find(function (num) {
return num % 2 === 0;
});
console.log(fristEven); // 2
}
// 배열에서 짝수 요소가 있으면 true, 없으면 false 반환하기
{
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const hasEven = numbers.some((num) => num % 2 === 0);
console.log(hasEven); // true
}
// 배열에서 모든 요소가 짝수라면 true, 아니라면 false 반환하기
{
const numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8];
const isAllEven = numbers.every((num) => num % 2 === 0);
console.log(isAllEven); // true
}
// 배열에 'banana' 요소가 포함되어 있으면 true, 없다면 false 반환하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"];
const hasBanana = fruits.includes("banana");
console.log(hasBanana); // true
}
// 배열의 'banana' 요소의 인덱스 구하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"];
const bananaIndex = fruits.indexOf("banana");
console.log(bananaIndex); // 1
}
// 배열에서 'apple' 요소와 마지막 인덱스 구하기
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "apple"];
const lastAppleIndex = fruits.lastIndexOf("apple");
console.log(lastAppleIndex); // 2
}
// 배열의 각 요소를 순회하면서 해당 색깔 출력하기
{
const color = ["red", "pink"];
color.forEach(function (key) {
console.log(`내가 좋아하는 색깔은 ${key}입니다!`);
});
}
아래와 같은 방법으로도 배열의 마지막 요소를 찾을 수 있다.
배열의 요소 개수에서 1을 빼면 마지막 요소의 인덱스가 된다.
const value = ["sieun", "Happy", "smile", "good"];
const last_value = value[value.length - 1];
console.log(last_value); // "good"
lenght-1을 하는 이유 : 배열의 인덱스가 0부터 시작하기 때문이다
예를 들어 [“A”, “B”, “C”, “D”]라는 배열이 있다면, 이 배열의 길이는 4이며 각 요소의 인덱스는 0부터 시작한다.
따라서 배열의 마지막 요소의 인덱스는 배열의 길이에서 1을 뺀 값인 것이다.
위를 참고하여 value 배열의 마지막에서 세 번째 요소(Happy)를 찾아보자
const value = ["sieun", "Happy", "smile", "good"];
const last_value = value[value.length - 3];
console.log(last_value); // "Happy"
4. 실습 및 응용하기
객체 배열인
items를 통해 응용을 해보자
const items = [
{ name: "Computer", price: 2100 },
{ name: "TV", price: 1820 },
{ name: "Book", price: 15 },
{ name: "Phone", price: 1600 },
{ name: "Coffee", price: 5 },
{ name: "Keyboard", price: 200 },
{ name: "Mouse", price: 140 },
];
① 가격이 300 이하인 요소들의 배열 만들기
const inexpensiveItems = items.filter((item) => item.price <= 300);
console.log(inexpensiveItems);
② items의 이름 또는 가격만 매핑해서 배열 만들기
const nameItems = items.map((item) => item.name);
console.log(nameItems);
③ 이름이 ‘Book’인 요소 찾기
const foundBook = items.find((item) => item.name === "Book");
console.log(foundBook);
④ items의 평균 가격 구하기
const total = items.reduce((acc, curr) => {
return acc + curr.price;
}, 0);
const average = total / items.length;
console.log(average);
⑤ items의 이름이 나열된 문자열 구하기
const names = items.map((item) => item.name).join(",");
console.log(names);

댓글남기기