[Spring-MVC] HTTP 요청 파라미터
[김영한 스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술]을 듣고 정리한 글입니다.
1. HTTP 요청 파라미터
HTTP 요청 메시지를 통해 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달하는 방법을 알아보자.
클라이언트에서 서버로 요청 데이터를 전달할 때는 주로 다음 3가지 방법을 사용한다.
① GET - 쿼리 파라미터
- /url?username=hello&age=20
- 메시지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- e.g., 검색, 필터, 페이징등에서 많이 사용하는 방식
② POST - HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 전달 username=hello&age=20
- e.g., 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용
③ HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
2. 쿼리 파라미터와 HTML Form
2.1 요청 파라미터 조회
GET, 쿼리 파라미터 전송
http://localhost:8080/request-param?username=hello&age=20
POST, HTML Form 전송
POST /request-param ...
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
username=hello&age=20
- GET 쿼리 파리미터 전송 방식이든, POST HTML Form 전송 방식이든 둘다 형식이 같으므로 구분없이 조회할 수 있다.
- 이것을 간단히 요청 파라미터(request parameter) 조회라 한다.
- 스프링으로 요청 파라미터를 조회하는 방법을 단계적으로 알아보자
2.2 Post Form 페이지 생성
먼저 테스트용 HTML Form을 만들어야 한다.
리소스는 /resources/static 아래에 두면 스프링 부트가 자동으로 인식한다.
main/resources/static/basic/hello-form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/request-param-v1" method="post">
username: <input type="text" name="username" /> age:
<input type="text" name="age" />
<button type="submit">전송</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Post Form 실행: http://localhost:8080/basic/hello-form.html
2.3 HttpServletRequest 사용
여기서는 단순히
HttpServletRequest가 제공하는 방식으로 요청 파라미터를 조회했다.
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
/**
* 반환 타입이 없으면서 이렇게 응답(response)에 값을 직접 집어넣으면, view 조회 X
*/
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v1")
public void requestParamV1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("age"));
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}
GET 실행: http://localhost:8080/request-param-v1?username=hello&age=20
서블릿을 이용해 HTTP 요청 데이터를 조회할 수 있지만, 스프링을 사용하면 더 깔끔하고 효율적으로 처리할 수 있다.
2.4 @RequestParam 사용
2.4.1 @RequestParam
스프링이 제공하는
@RequestParam을 사용하면 요청 파라미터를 매우 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
- @RequestParam 역할
@RequestParam String username→ 쿼리 파라미터username값을username변수에 저장@RequestParam int age→ 쿼리 파라미터age값을age변수에 저장- 타입 변환도 자동으로 수행됨 (age가 int 타입이지만 String → int 변환됨)
/**
* @RequestParam 사용
* - 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩
* @ResponseBody 추가
* - View 조회를 무시하고, HTTP message body에 직접 해당 내용 입력
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v2")
public String requsetParamV2(
/* @RequestParam의 name(value) 속성이 파라미터 이름으로 사용 */
@RequestParam("username") String memberName,
@RequestParam("age") int memberAge) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", memberName, memberAge);
return "ok";
}
실행: http://localhost:8080/request-param-v2?username=hello&age=20
HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 @RequestParam(name=”xx”) 생략이 가능하다.
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v3")
public String requestParamV3(
@RequestParam String username,
@RequestParam int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}
String, int 등의 단순 타입이면
@RequestParam도 생략이 가능하다.
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v4")
public String requestParamV4(String username, int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}
@RequestParam 애노테이션을 생략하면 스프링 MVC는 내부에서 required=false 를 적용한다.
requestParamV4 처럼 애노테이션을 완전히 생략해도 되는데, 너무 없는 것도 과하다는 강사님의 의견!
`@RequestParam` 이 있으면 명확하게 요청 파라미터에서 데이터를 읽는 것을 알 수 있기 때문이다.
2.4.2 파라미터 필수 여부 - requestParamRequired
@RequestParam의 기본 동작은 요청 파라미터가 반드시 있어야 한다.
- 만약
age나username을 전달하지 않으면 400 Bad Request 오류가 발생한다. - 하지만,
required=false를 설정하면 해당 파라미터가 없어도 요청이 가능하며, null이 들어간다./request-param-required?username=: 파라미터 이름만 있고 값이 없는 경우 → 빈문자로 통과
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-required")
public String requestParamRequired(
@RequestParam(required = true) String username,
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}
@RequestParam.required- 파라미터 필수 여부
- 기본값이 파라미터 필수(
true)이다.
/request-param-required요청username이 없으므로 400 예외가 발생한다.
기본형(primitive)에 null 입력
/request-param요청@RequestParam(required = false) int agenull을int에 입력하는 것은 불가능(500 예외 발생)- 따라서
null을 받을 수 있는Integer로 변경하거나, 또는 다음에 나오는defaultValue사용
2.4.3 기본 값 적용 - requestParamDefault
요청 파라미터가 없을 경우,
defaultValue를 사용하여여 기본 값을 적용할 수 있다.
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-default")
public String requestParamDefault(
@RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue = "guest") String username,
@RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "-1") int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}
이미 기본 값이 있기 때문에 required 는 의미가 없다.
defaultValue 는 빈 문자의 경우에도 설정한 기본 값이 적용된다. /request-param-default?username=
2.4.4 파라미터를 Map으로 조회하기 - requestParamMap
/**
* @RequestParam Map, MultiValueMap
* Map(key=value)
* MultiValueMap(key=[value1, value2, ...]) ex) (key=userIds, value=[id1, id2])
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-map")
public String requestParamMap(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> paramMap) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", paramMap.get("username"),
paramMap.get("age"));
return "ok";
}
@RequestParam Map |
Map(key=value) |
|---|---|
@RequestParam MultiValueMap |
MultiValueMap(key=[value1, value2, ...] e.g., (key=userIds, value=[id1, id2]) |
파라미터의 값이 1개가 확실하다면 Map 을 사용해도 되지만, 그렇지 않다면 MultiValueMap 을 사용하자. (보통 1개를 씀)
2.5 @ModelAttribute
실제 개발을 하면 요청 파라미터를 받아서 필요한 객체를 만들고 그 객체에 값을 넣어주어야 한다.
보통 다음과 같이 코드를 작성할 것이다
@RequestParam String username;
@RequestParam int age;
HelloData data = new HelloData();
data.setUsername(username);
data.setAge(age);
스프링은 이 과정을 완전히 자동화해주는 @ModelAttribute 기능을 제공한다.
먼저 요청 파라미터를 바인딩 받을 객체를 만들자
2.5.1 HelloData
package hello.springmvc.basic;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class HelloData {
private String username;
private int age;
}
롬복 @Data : @Getter , @Setter , @ToString , @EqualsAndHashCode , @RequiredArgsConstructor 를 자동으로 적용해준다.
2.5.2 @ModelAttribute 적용
/**
* @ModelAttribute 사용
* 참고: model.addAttribute(helloData) 코드도 함께 자동 적용됨, 뒤에 model을 설명할 때 자세히 설명
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/model-attribute-v1")
public String modelAttributeV1(@ModelAttribute HelloData helloData) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", helloData.getUsername(), helloData.getAge());
return "ok";
}
마치 마법처럼 HelloData 객체가 생성되고, 요청 파라미터의 값도 모두 들어가 있다.
스프링MVC는
@ModelAttribute가 있으면 다음을 실행한다.
HelloData객체를 생성한다.- 요청 파라미터의 이름으로
HelloData객체의 프로퍼티를 찾는다. 그리고 해당 프로퍼티의 setter를 호출해서 파라미터의 값을 입력(바인딩) 한다. - e.g., 파라미터 이름이
username이면setUsername()메서드를 찾아서 호출하면서 값을 입력한다.
프로퍼티
- 객체에
getUsername(),setUsername()메서드가 있으면, 이 객체는username이라는 프로퍼티를 가지고 있다. username프로퍼티의 값을 변경하면setUsername()이 호출되고, 조회하면getUsername()이 호출된다.- getXxx → xxx, setXxx → xxx
class HelloData {
getUsername();
setUsername();
}
바인딩 오류
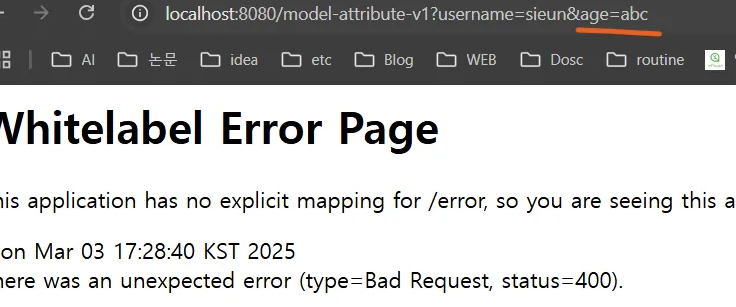
age=abc 처럼 숫자가 들어가야 할 곳에 문자를 넣으면 BindException 이 발생한다. 이런 바인딩 오류를 처리하는 방법은 검증 부분에서 다룬다.
2.5.3 @ModelAttribute 생략
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/model-attribute-v2")
public String modelAttributeV2(HelloData helloData) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", helloData.getUsername(),
helloData.getAge());
return "ok";
}
@ModelAttribute 는 생략할 수 있다.
그런데 @RequestParam 도 생략할 수 있으니 혼란이 발생할 수 있다.
- 스프링은 해당 생략시 다음과 같은 규칙을 적용한다.
String,int,Integer같은 단순 타입 =@RequestParam- 나머지 =
@ModelAttribute(argument resolver 로 지정해둔 타입 외)
3. HTTP 요청 메시지
3.1 단순 텍스트
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
요청 파라미터와 다르게, HTTP 메시지 바디를 통해 데이터가 직접 넘어오는 경우는 @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute 를 사용할 수 없다.
(물론 HTML Form 형식으로 전달되는 경우는 요청 파라미터로 인정된다.)
RequestBodyStringController
- 먼저 가장 단순한 텍스트 메시지를 HTTP 메시지 바디에 담아서 전송하고, 읽어보자.
- HTTP 메시지 바디의 데이터를 InputStream 을 사용해서 직접 읽을 수 있다.
- 다양한 방법이 있지만, 자주 사용하는 방식만 다룰 것이다. (다른 방법은 강의 참고)
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestBodyStringController {
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-string-v4")
public String requestBodyStringV4(@RequestBody String messageBody) {
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
return "ok";
}
}
-
@RequestBody
@RequestBody를 사용하면 HTTP 메시지 바디 정보를 편리하게 조회할 수 있다. 헤더 정보가 필요하다면HttpEntity를 사용하거나@RequestHeader를 사용하면 된다.- 이렇게 메시지 바디를 직접 조회하는 기능은 요청 파라미터를 조회하는
@RequestParam,@ModelAttribute와는 전혀 관계가 없다.
- 요청 파라미터 vs HTTP 메시지 바디
- 요청 파라미터를 조회하는 기능:
@RequestParam,@ModelAttribute - HTTP 메시지 바디를 직접 조회하는 기능:
@RequestBody
- 요청 파라미터를 조회하는 기능:
- @ResponseBody
@ResponseBody를 사용하면 응답 결과를 HTTP 메시지 바디에 직접 담아서 전달할 수 있다.- 이 경우에도 view를 사용하지 않는다.
스프링MVC 내부에서 HTTP 메시지 바디를 읽어서 문자나 객체로 변환해서 전달해주는데,
이때 HTTP 메시지 컨버터( HttpMessageConverter )라는 기능을 사용한다.
3.2 JSON
이번에는 HTTP API에서 주로 사용하는 JSON 데이터 형식을 조회해보자.
역시 다양한 방법이 있지만, 자주 사용하는 방식만 다룰 것이다. (다른 방법은 강의 참고)
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
/**
* {"username":"hello", "age":20}
* content-type: application/json
*/
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestBodyJsonController {
/**
* @RequestBody 생략 불가능(@ModelAttribute 가 적용되어 버림)
* HttpMessageConverter 사용 -> MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter (content-type:application/json)
*
* @ResponseBody 적용
* - 메시지 바디 정보 직접 반환(view 조회X)
* - HttpMessageConverter 사용 -> MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 적용(Accept:application/json)
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-json-v5")
public HelloData requestBodyJsonV5(@RequestBody HelloData data) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge());
return data;
}
}
@ResponseBody응답의 경우에도@ResponseBody를 사용하면 해당 객체를 HTTP 메시지 바디에 직접 넣어줄 수 있다.@RequestBody객체 파라미터@RequestBody HelloData data@RequestBody에 직접 만든 객체를 지정할 수 있다.
@RequestBody요청- JSON 요청 → HTTP 메시지 컨버터 → 객체
@ResponseBody응답- 객체 → HTTP 메시지 컨버터 → JSON 응답
@RequestBody는 생략 불가능
- 스프링은
@ModelAttribute,@RequestParam과 같은 해당 애노테이션을 생략시 다음과 같은 규칙을 적용한다.- String , int , Integer 같은 단순 타입 =
@RequestParam - 나머지 =
@ModelAttribute(argument resolver 로 지정해둔 타입 외)
- String , int , Integer 같은 단순 타입 =
따라서 이 경우 HelloData에 @RequestBody를 생략하면 @ModelAttribute 가 적용되어버린다.
HelloData data → @ModelAttribute HelloData data
따라서 생략하면 HTTP 메시지 바디가 아니라 요청 파라미터를 처리하게 된다.
HttpEntity , @RequestBody 를 사용하면 HTTP 메시지 컨버터가 HTTP 메시지 바디의 내용을 우리가 원하는 문자나 객체 등으로 변환해준다.
- HTTP 요청시에
content-type이application/json인지 확인해야 한다. - 그래야 JSON을 처리할 수 있는 HTTP 메시지 컨버터가 실행된다
4. HTTP 메시지 컨버터 간단히 알아보기
HTTP 메시지 컨버터(HttpMessageConverter) 는 스프링 MVC(Spring MVC) 에서 HTTP 요청 메시지의 바디(Body)를 특정 객체로 변환하거나, 반대로 특정 객체를 HTTP 응답 메시지의 바디에 변환할 때 사용되는 인터페이스이다.
주로 @RequestBody, @ResponseBody, @RestController 사용 시 자동으로 동작하며, 클라이언트와 서버 간의 데이터를 편리하게 변환할 수 있도록 도와준다.
- 스프링 MVC는 다음의 경우에 HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 적용한다.
- HTTP 요청:
@RequestBody,HttpEntity(RequestEntity), - HTTP 응답:
@ResponseBody,HttpEntity(ResponseEntity
- HTTP 요청:

댓글남기기